🔒 7 Powerful Ways to Prevent Directory Traversal Attack in Laravel
What is a Directory Traversal Attack in Laravel?
A directory traversal attack in Laravel is a type of file path manipulation where a user attempts to access directories and files outside the intended folder structure. This is typically done by inserting sequences like ../ into input fields or URLs, allowing attackers to navigate the server’s file system in ways they shouldn’t.

These attacks are dangerous because they can lead to:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive files like
.env - Leakage of source code or credentials
- Complete server compromise if critical configs are exposed
Despite Laravel being one of the most secure PHP frameworks, incorrect handling of user input in file paths can open doors to such vulnerabilities.
How Directory Traversal Works in Laravel
Imagine you have a download feature for users to access documents:
// web.php
Route::get('/download/{filename}', [FileController::class, 'download']);// FileController.php
public function download($filename)
{
$filePath = storage_path('app/files/' . $filename);
if (file_exists($filePath)) {
return response()->download($filePath);
} else {
abort(404);
}
}⚠️ Dangerous Exploit
An attacker could simply do this:
https://yourapp.com/download/../../.envAnd retrieve sensitive data from the .env file, including:
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=secret
MAIL_PASSWORD=mailpassThis attack works because there’s no sanitization or validation in place.
Real-World Impacts of Directory Traversal Attacks
Some serious consequences include:
- 🔓 Database Credentials Leak: Your
.envfile stores DB usernames, passwords, and keys. - 🕵️ Source Code Exposure: Attackers can access controller files or
.blade.phptemplates. - 🧠 Attack Chain Facilitation: With enough info, attackers can chain attacks (e.g., RCE or SQLi).
- 🧨 Full Server Takeover: Access to system configuration or SSH keys can result in total compromise.
Detecting Directory Traversal: Signs & Symptoms
Watch out for these patterns in your logs:
- URL patterns like
../,%2e%2e/, or similar encoded strings. - High frequency of file download requests.
- Access to unexpected file types via user input (e.g.,
.env,.log).
🚨 Dangerous Laravel Misconfigurations
If you’re using code like this to read user-generated files:
public function viewLog($file) {
$filePath = storage_path("logs/{$file}");
return file_get_contents($filePath);
}An attacker might attempt:
/viewLog/../../.envOr even URL-encoded:
/viewLog/%2e%2e/%2e%2e/.env7 Proven Ways to Prevent Directory Traversal Attack in Laravel
✅ 1. Use Whitelisting for Allowed File Names
Rather than trusting user input, define a list of files they’re allowed to access:
$allowedFiles = ['manual.pdf', 'guide.pdf', 'invoice123.pdf'];
if (!in_array($filename, $allowedFiles)) {
abort(403, 'Access denied.');
}✅ 2. Validate File Names with Regex
if (!preg_match('/^[a-zA-Z0-9_\-\.]+$/', $filename)) {
abort(400, 'Invalid file name.');
}This ensures no traversal patterns like ../ sneak in.
✅ 3. Normalize Paths with realpath()
$base = realpath(storage_path('app/files'));
$requested = realpath($base . '/' . $filename);
if (strpos($requested, $base) !== 0) {
abort(403, 'Hacking attempt detected.');
}✅ 4. Use Laravel Storage API
Laravel provides secure APIs to access files:
if (Storage::disk('local')->exists("public/files/{$filename}")) {
return Storage::download("public/files/{$filename}");
}
abort(404);This ensures access is scoped and well-handled.
✅ 5. Replace Traversal Tokens in Input
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
$sanitized = Str::replace(['../', '..\\'], '', $filename);Basic, but helps eliminate direct traversal characters.
✅ 6. Log Suspicious File Access Attempts
Keep track of unauthorized access attempts:
if (!file_exists($requested)) {
Log::warning("Suspicious file request: " . $filename);
abort(404);
}✅ 7. Scan for Vulnerabilities Automatically
Use our Website Vulnerability Scanner to detect directory traversal risks in your Laravel application.
Image: Screenshot of the webpage of our free tool
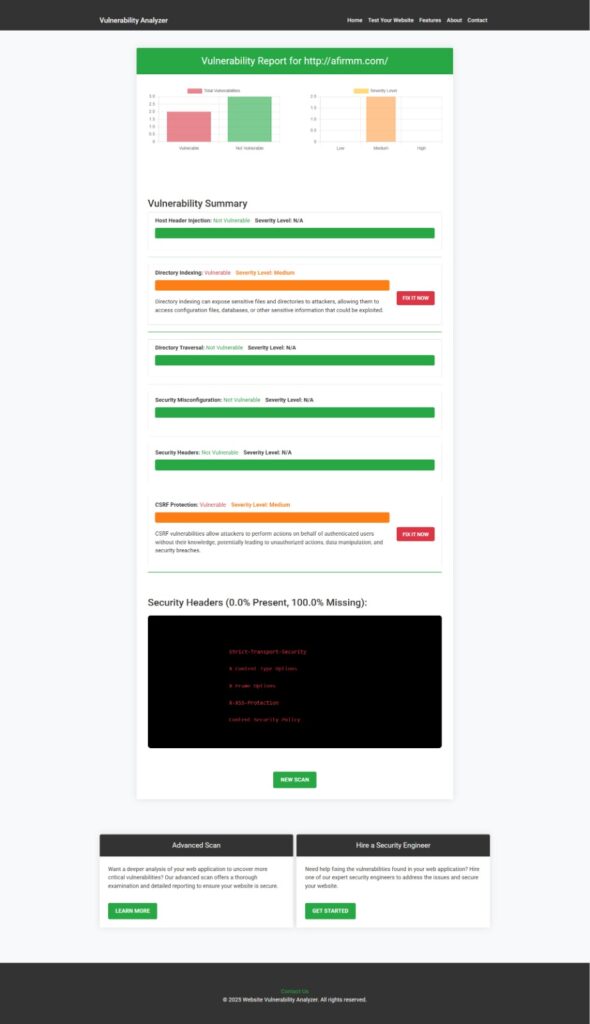
Example Report of Vulnerability Detection
After scanning a Laravel application with our tool, here’s what a report might look like:
Image: Vulnerability assessment report to check Website Vulnerability
Laravel Secure File Upload Example
Avoid letting users upload files to arbitrary paths:
$request->validate([
'file' => 'required|file|mimes:pdf,docx,jpg|max:2048'
]);
$path = $request->file('file')->store('public/uploads');Never let users choose the directory manually.
💡 Are you a developer or an IT agency?
You can now offer our pentesting services under your brand or earn referral commissions.
👉 Explore our Agency Partner Program:
https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Related Articles You Should Check Out
- 🔐 Prevent XXE Injection in Laravel
- 📘 Java Web App Penetration Testing
- 🛡️ Prevent XML Injection in OpenCart
- ⛔ File Inclusion Vulnerability in Laravel
- 💬 Contact Us
Bonus for frontend security:
Final Thoughts
Directory traversal attack in Laravel is more common than developers realize. Fortunately, with Laravel’s modern toolset and a good understanding of path sanitization, these attacks can be easily mitigated.
Make sure your Laravel application is:
- Validating all user inputs properly
- Using safe APIs for file access
- Regularly audited for Website Security check using automated tools
By taking proactive steps, you can secure your Laravel app against one of the oldest and still widely exploited vulnerabilities in web development.
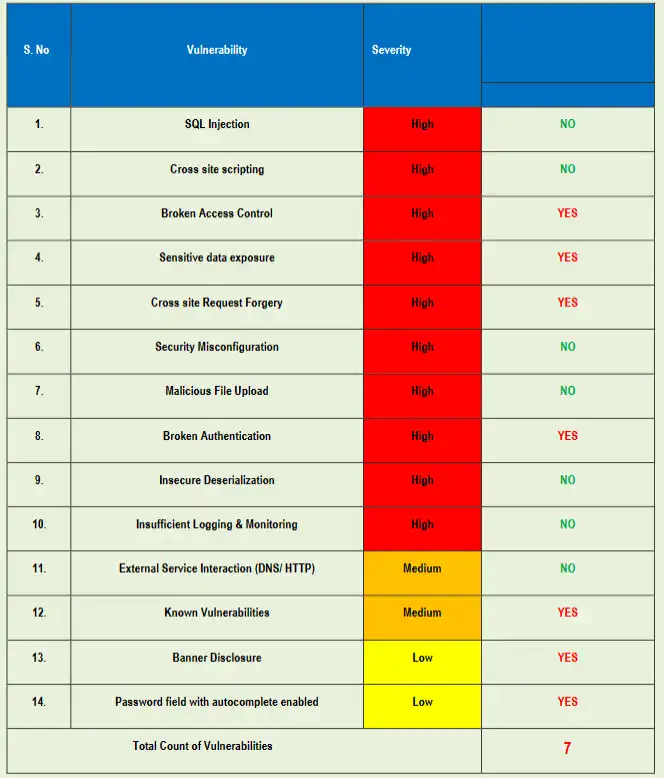

Pingback: Prevent Cross-Site Scripting in React.js with Best 7 Ways