5 Essential Steps to Prevent Attacks on Command Injection in OpenCart
Introduction
Command injection attacks pose a significant threat to e-commerce platforms like OpenCart. These attacks occur when malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities to execute arbitrary commands on the host operating system, potentially compromising the entire application. Understanding and mitigating these risks is crucial for maintaining a secure online store.

What is a Command Injection Attack?
A command injection attack involves executing arbitrary commands on a host operating system through a vulnerable application. Attackers exploit insufficient input validation to inject malicious commands, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and system compromise.
📌 Key Risks of Command Injection:
- Unauthorized system access – Attackers can execute OS-level commands.
- Data breaches – Sensitive customer data can be stolen.
- Website defacement – Attackers may modify website content.
- Server compromise – The entire hosting environment can be taken over.
Example of a Basic Command Injection Attack
An attacker might exploit a vulnerable OpenCart admin panel using a web request like:
https://example.com/admin/index.php?route=system/backup&file=backup.sql;cat /etc/passwdHere, the cat /etc/passwd command is injected, potentially exposing sensitive system files.
How Command Injection Affects OpenCart
OpenCart, being a widely used e-commerce platform, can be susceptible to command injection attacks if not properly secured.
Common Causes of Vulnerabilities in OpenCart
- Inadequate Input Validation:
- User input is not properly sanitized, allowing arbitrary commands to be executed.
- Unsafe Use of System Functions:
- Using PHP functions like
exec(),shell_exec(), orsystem()with unsanitized inputs.
- Using PHP functions like
- Vulnerable Third-Party Extensions:
- Many OpenCart plugins introduce security flaws due to poor coding practices.
- Misconfigured Server Settings:
- Weak security configurations can make OpenCart susceptible to exploitation.
5 Essential Steps to Prevent Command Injection in OpenCart
1. Implement Strict Input Validation
Ensuring all user inputs are validated against expected patterns is critical. Reject any input that does not conform to the anticipated format.
✅ Secure Example:
// Validate product ID as an integer
$product_id = filter_input(INPUT_GET, 'product_id', FILTER_VALIDATE_INT);
if ($product_id === false) {
exit('Invalid product ID');
}❌ Insecure Example:
// Directly using user input without validation
$product_id = $_GET['product_id'];
$sql = "SELECT * FROM products WHERE id = $product_id";
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);2. Avoid Direct Execution of System Commands
Refrain from using PHP functions that execute system commands, such as exec(), shell_exec(), and system() with user inputs.
✅ Secure Example:
// Avoid using exec() with user input
$filename = escapeshellarg($user_input);
exec("ls -l $filename");❌ Insecure Example:
// Using user input in exec() (Vulnerable)
exec("rm -rf " . $_GET['dir']);3. Use Prepared Statements for Database Queries
Prepared statements help prevent injection attacks in SQL queries by ensuring that user inputs are treated as data, not executable code.
✅ Secure Example:
$stmt = $db->prepare('SELECT * FROM products WHERE id = ?');
$stmt->bind_param('i', $product_id);
$stmt->execute();❌ Insecure Example:
$sql = "SELECT * FROM products WHERE id = " . $_GET['product_id'];
$result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);4. Regularly Update OpenCart and Extensions
Outdated OpenCart versions and third-party extensions often contain security vulnerabilities. Regular updates help mitigate these risks.
✅ Best Practices for Updating OpenCart:
- Enable automatic security patches if available.
- Download updates only from the official OpenCart marketplace.
- Remove unused or outdated extensions to reduce the attack surface.
5. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Regular penetration testing and security assessments can help detect vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
🔍 Use our Free Website Security Scanner
At Pentest Testing Corp, we provide a free website vulnerability scanner to help assess your website’s security.
Additionally, our free scanner generates a detailed vulnerability assessment report to check website vulnerability and highlight security risks in your OpenCart store.
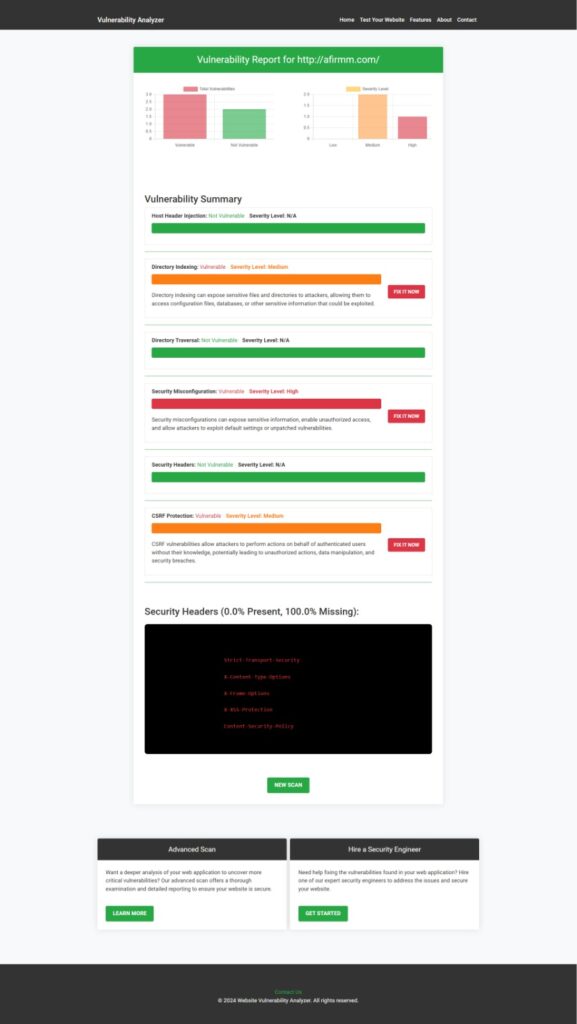
Real-World Example: OpenCart 3.0.2.0 Vulnerability
In OpenCart version 3.0.2.0, a directory traversal vulnerability was identified, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code.
Exploit Example:
curl -X GET "https://example.com/admin/index.php?route=system/backup&file=../../../../etc/passwd"This command retrieves sensitive system files due to improper path validation.
Fix:
Update OpenCart to the latest version and validate file paths to prevent directory traversal.
💡 Are you a developer or an IT agency?
You can now offer our pentesting services under your brand or earn referral commissions.
👉 Explore our Agency Partner Program:
https://www.pentesttesting.com/offer-cybersecurity-service-to-your-client/
Conclusion
Protecting your OpenCart store from command injection attacks requires strict input validation, cautious coding practices, and regular security assessments. Implementing these 5 essential steps will significantly reduce the risk of exploitation and keep your e-commerce platform secure.
✅ Stay proactive in securing your online store. For more insights, check out our related guides:
- Prevent DNS Rebinding Attack in OpenCart
- Prevent Buffer Overflow in OpenCart
- HTTP Response Splitting in OpenCart
- Prevent Race Condition in TypeScript
Want more cybersecurity tips? Visit our blog for the latest updates! 🚀

