DNS Rebinding Attack in OpenCart: Protect Your Store from Cyber Threats
What is a DNS Rebinding Attack?
A DNS rebinding attack is a type of cyber attack that manipulates the Domain Name System (DNS) to bypass the same-origin policy enforced by web browsers. This attack allows an attacker to gain unauthorized access to internal networks by tricking a victim’s browser into sending malicious requests.

In OpenCart, a DNS rebinding attack can:
- Access internal admin interfaces
- Steal customer payment and personal data
- Modify store settings or inventory
- Inject malicious scripts into your website
This type of attack can be dangerous if your OpenCart store is not properly configured with security measures.
How Does a DNS Rebinding Attack Work?
A DNS rebinding attack exploits how DNS resolution works to trick the browser into making unauthorized requests. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Step 1: The Attacker Sets Up a Malicious Domain
The attacker registers a domain (e.g., malicious.com) and configures a DNS server that initially resolves this domain to their own controlled server.
Step 2: The Victim Visits the Malicious Website
When the victim loads malicious.com, a JavaScript payload is executed in the browser.
Step 3: The DNS Server Rebinds the Domain to an Internal IP
The attacker modifies the DNS response so that malicious.com now resolves to an internal IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
Step 4: Unauthorized Requests are Sent
Since the browser believes it is communicating with malicious.com, it bypasses the same-origin policy and sends malicious requests to internal services.
Impact of DNS Rebinding on OpenCart
In an OpenCart environment, a successful DNS rebinding attack can result in:
🔴 Unauthorized access to the admin panel
🔴 Customer data theft, including credit card details
🔴 Store defacement and unauthorized product modifications
🔴 Malicious JavaScript injection
Because OpenCart relies on APIs, cookies, and admin panels, a DNS rebinding attack can be devastating if security measures are not in place.
How to Prevent DNS Rebinding Attack in OpenCart
To protect your OpenCart store from DNS rebinding attacks, follow these essential security practices.
1. Implement DNS Pinning
DNS pinning prevents browsers from accepting a new DNS resolution for a domain during a session. Most modern browsers have built-in protection, but it’s still essential to:
✅ Ensure customers use updated web browsers
✅ Set short DNS Time-To-Live (TTL) values
✅ Use Content Security Policy (CSP) headers
2. Validate Host Headers in OpenCart
Ensuring your OpenCart store only accepts valid Host headers can help prevent unauthorized requests.
Example: Apache Configuration
Add the following rules in your .htaccess file:
<If "%{HTTP_HOST} != 'yourdomain.com'">
Require all denied
</If>Example: OpenCart PHP Validation
Modify index.php to reject requests from unknown hosts:
<?php
$allowed_host = 'yourdomain.com';
if ($_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] !== $allowed_host) {
header($_SERVER['SERVER_PROTOCOL'] . ' 400 Bad Request');
exit('Invalid Host Header');
}
?>This simple Host header validation can block DNS rebinding attempts.
3. Restrict Internal API Access
If your OpenCart store exposes API endpoints, attackers may try to exploit them through DNS rebinding. You can restrict API access by:
✅ Blocking private IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x)
✅ Allowing only trusted referrers
✅ Using authentication tokens
Example: Prevent API Access to Internal IPs
Modify OpenCart’s API authentication function (system/library/cart.php):
$blocked_ips = ['127.0.0.1', '192.168.1.1', '10.0.0.1'];
if (in_array($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR'], $blocked_ips)) {
die('Access denied.');
}This will block API access from internal addresses, preventing unauthorized requests.
4. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF can detect DNS rebinding attack patterns and block malicious requests. Popular cloud-based WAFs include:
✔ Cloudflare WAF
✔ AWS WAF
✔ ModSecurity (for Apache/Nginx)
5. Network Segmentation: Isolate Your Admin Panel
To prevent attackers from reaching sensitive resources, host your OpenCart admin panel on a separate subdomain (e.g., admin.yourstore.com) and restrict access to only trusted IPs.
Example: Nginx Restrict Admin Panel Access
location /admin {
allow 203.0.113.1; # Replace with your IP
deny all;
}This ensures only your IP can access the admin dashboard.
6. Monitor for Suspicious DNS Activity
Set up DNS logging and monitoring to detect:
✔ Frequent DNS record changes
✔ Unusual domain resolutions to internal IPs
✔ Sudden spikes in DNS requests
Tools like Wireshark, Security Onion, or Splunk can help track malicious DNS behavior.
7. Regularly Scan Your OpenCart Store for Vulnerabilities
Perform regular security scans to detect vulnerabilities that could be exploited in a DNS rebinding attack.
🔍 Use our Free Website Security Scanner:
Check your OpenCart store for weaknesses using our Website Security Checker.
You can also view a sample Website Vulnerability Report generated by our tool:
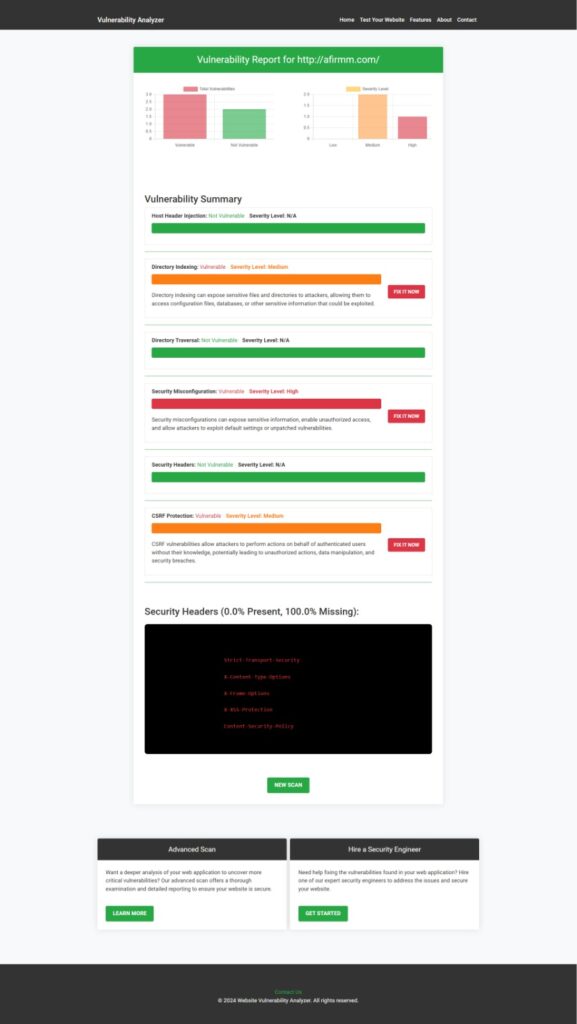
Analyze the Vulnerability report generated by our tool to check Website Vulnerability.
Final Thoughts
Protecting your OpenCart store from DNS rebinding attacks is essential for ensuring customer data security and preventing unauthorized access. By implementing proper server configurations, API restrictions, and Host header validation, you can effectively mitigate the risks.
Explore More OpenCart Security Guides:
- 🔗 Prevent Race Conditions in OpenCart
- 🔗 Prevent Host Header Injection in OpenCart
- 🔗 Prevent Command Injection in OpenCart
- 🔗 Learn About Transport Layer Security
- 🔗 Check More Cybersecurity Blogs
By staying vigilant and applying these 7 security techniques, you can fortify your OpenCart store against DNS rebinding attacks. 🚀


Thank you so much for your kind words and thoughtful feedback! 😊 We’re really glad you enjoyed the writing and structure of the blog post. Everything we publish is custom-written by our team to share real insights and practical advice from hands-on experience. It means a lot to hear that it’s making a positive impact! Stay tuned—we’ve got more security-focused content on the way. Feel free to subscribe or drop by anytime to share your thoughts! 💬🔐